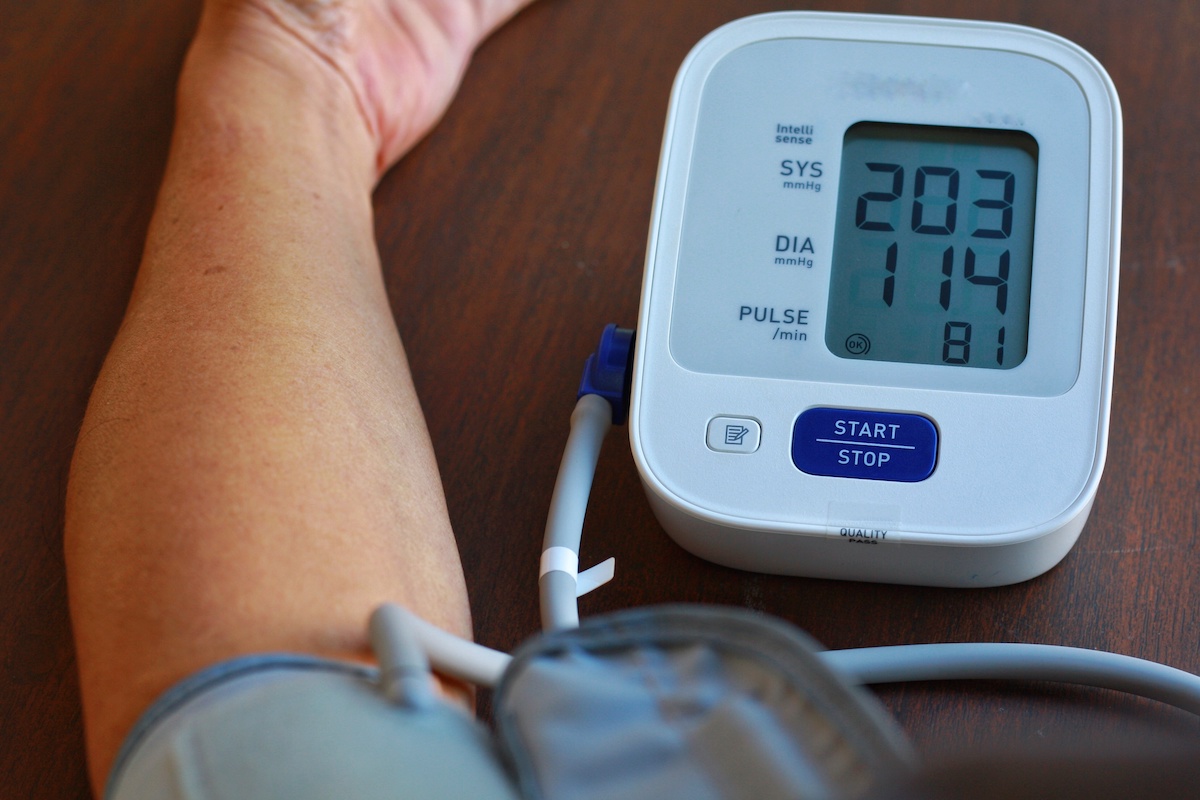
Signs, Management, and Avoidance
Millions of individuals worldwide suffer from high blood pressure, also referred to as hypertension in medical terminology. Even though it is very common, many people are not aware of their illness until serious health problems occur. All of the information you require regarding high blood pressure medication, symptoms, blood pressure monitors, what hypertension is, diet, treatment, causes, blood pressure readings, blood pressure chart by age, high blood pressure and heart disease, and stages of hypertension will be covered in this extensive guide.
Symptoms
The fact that hypertension frequently shows no symptoms is one of its most harmful features. But when signs of high blood pressure do appear, they could include:
- A Headaches
- Bleeding noses
- Breathlessness
- Pain in the chest
- Issues with vision
Early detection of high blood pressure symptoms can help avoid more catastrophic consequences, such as heart disease and high blood pressure.
Stages of Hypertension
Different stages of hypertension dictate the severity of the problem and the kind of treatment needed for high blood pressure:
- Below 120/80 mmHg is normal.
- 120–129/<80 mmHg elevated
- Hypertension in Stage 1: 130–139/80–89 mmHg
- Hypertension in Stage 2: ≥140/90 mmHg
- Crisis of hypertension: >180/120 mmHg (get care right now)
Patients and physicians can take prompt action when they are aware of these stages of hypertension.
Causes of Hypertension
The following are some of the causes of hypertension:
- Genetics
- Being overweight
- Smoking
- Consuming too much salt
- Absence of exercise
- Prolonged stress
- Kidney issues
Understanding the origins of hypertension can help inform effective diet and treatment plans as well as lifestyle modifications.
Age-Based Blood Pressure Chart
Assessing health risks requires an understanding of the blood pressure chart by age. Because our arteries stiffen with age, blood pressure levels may normally rise. A brief overview of general healthy ranges is provided below:
| Age Group | Normal Blood Pressure |
|---|---|
| 18–39 years | 119/79 mmHg |
| 40–59 years | 124/79 mmHg |
| 60+ years | 133/83 mmHg |
Methods for Interpreting Blood Pressure Measurements
The first step in controlling hypertension is to comprehend your blood pressure levels. For instance:
- Systolic (upper number): Heartbeat pressure
- Diastolic (bottom number): Heart resting pressure
Precise blood pressure measurements shed light on your health and aid in tracking how well a diet or medication for high blood pressure is working.
Heart disease with high blood pressure
High blood pressure and heart disease are two of the most serious effects of uncontrolled hypertension. Long-term elevated blood pressure can result in:
- Heart attacks
- A stroke
- Heart failure
- Aneurysms
Heart disease and high blood pressure are closely related because the heart must work harder to pump blood, which over time damages organs and arteries.
Medication for High Blood Pressure
Medication for high blood pressure is frequently suggested by doctors when lifestyle changes are insufficient. Typical kinds include of:
- Diuretics: Assist the kidneys in eliminating extra water and salt.
- Beta-blockers: Lower blood flow and heart rate.
- Blood vessels are relaxed by ACE inhibitors.
- Calcium channel blockers: Stop calcium from getting into blood vessel and cardiac cells.
Maintaining control of the condition and preventing high blood pressure and heart disease depend on taking high blood pressure medication on a regular basis.
Blood Pressure Monitor:
The Significance of It
One of the most important tools for controlling pressure is a device to track blood pressure. It assists people in monitoring their blood pressure every day and evaluating the effectiveness of blood pressure-lowering drugs or treatments.
Easy to use and reasonably priced are home blood pressure monitors. Select one that has been endorsed by medical experts and verified for accuracy.
Diet for Hypertension
A carefully thought-out diet for hypertension can lower blood pressure considerably.
- Whole grains
- Dairy products with little fat
- vegetables and fruits
- Lean proteins
- Decreased consumption of sodium
A diet for hypertension prioritises minerals including calcium, magnesium, and potassium while limiting processed foods.
Lifestyle Advice for Preventing High Blood Pressure
- Spend 30 minutes a day exercising.
- Keep your weight in check.
- Don’t drink too much.
- Obtain 7 to 9 hours of rest.
- Use therapy or meditation to keep an eye on stress.
Long-term control is aided by putting these practices into practice in conjunction with a hypertensive diet and routine blood pressure checks.
In conclusion,
For early intervention, it is essential to comprehend what hypertension is and identify its signs. It can be easier to spot changes if you regularly use a blood pressure monitor, record your readings, and refer to the blood pressure chart by age. Effective treatment of high blood pressure is based on a combination of lifestyle modifications, a healthy diet, and, when necessary, high blood pressure medication, regardless of the stage of the disease.
Recall that heart disease and high blood pressure are both primarily caused by uncontrolled hypertension. Complications can be avoided and a longer, healthier life can result from early intervention, appropriate monitoring, and regular therapy.